What is a Wav File: Explained
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format), sometimes referred to as WAVE, is one of the oldest and most widely used audio encoding formats in existence. Developed by Microsoft and IBM, its primary purpose was to facilitate the playback of audio on personal computers. Over the years, it has evolved into the preferred format for archival digital audio due to its uncompressed nature, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of WAV files, exploring their origins, functionalities, and alternatives.
Part 1: Origins and Evolution of WAV Files
The origins of the WAV file format date back to the early 1990s. when IBM and Microsoft collaborated to define a format for sound files compatible with the limited processing power and memory of personal computers at the time.
Unlike compressed formats, which could have reduced file sizes but would burden processors with significant computational tasks, WAV files store each audio sample directly as its bit value. This simplistic approach was suitable for short sound effects rather than longer audio compositions.
While WAV files may seem primitive compared to modern audio formats, their simplicity has earned them a niche as an archival and editing format. Despite lacking a formal standard, the format's widespread adoption and compatibility have solidified its position in the realm of digital audio.
Technical Specifications of WAV Files
At its core, WAV files adhere to the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF), a general-purpose format for packaging data and metadata.
With in this structure, WAV files consist of various "chunks", each designated for specific types of information such as encoded audio, timestamps, and encoding parameters. While WAV shares similarities with the AIFF format used by Apple, they are not compatible with each other.
Over time, advancements such as the Wave Format Extensible (WFX) introduced by Microsoft in Windows 2000 have enhanced WAV's capabilities, particularly in supporting multichannel audio and speaker positioning information.
Despite the absence of a formal standard, WAV files can be created and played without the need for licensing, although certain codecs may require proprietary information.
Part 2: What Are WAV Files Used for?
WAV files offer broad support among desktop music players due to their ease of implementation. Most music players on Windows systems natively support WAV, while cross-platform players like VLC provide compatibility across different operating systems.
However, mobile applications capable of playing WAV files are less common, primarily due to their large file sizes and the availability of more space-efficient audio formats for mobile devices.
Technical Composition and Flexibility
Technically speaking, WAV files adhere to the container-codec paradigm, wherein the container establishes the file structure and metadata, while the codec handles the encoding and decoding of audio data.
The default codec for WAV files is LPCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulation). It is a lossless compression algorithm that preserves the original audio quality. While other codecs like ADPCM (Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation) exist, they are less common.
One of the defining characteristics of WAV files is their flexibility in terms of audio parameters. They can accommodate thousands of channels, an unlimited number of bits per sample. It supports high sample rates far beyond the range of human hearing.
Additionally, WAV files can include various metadata, making them suitable for archival purposes and metadata-rich applications.
Broadcast WAV and Beyond
The European Broadcast Union introduced Broadcast Wave Format (BWF) as a refinement of the WAV format, primarily for exchanging audio files in broadcast environments. BWF files include additional metadata, such as originator information and creation timestamps, enhancing their utility for preservation projects. Variants like RF64 address limitations such as the 4 GB file size cap, further expanding WAV's capabilities.
Alternatives and Conversions
While WAV files excel in preserving audio fidelity, their large file sizes make them impractical for everyday use. Compressed formats like FLAC(Free Lossless Audio Codec) offer comparable quality with significantly smaller file sizes, making them ideal for storage and distribution. Additionally, lossy formats like MP3 and AAC provide even greater compression at the expense of some audio quality, suitable for streaming and mobile playback.
Part 3: Convert WAV to Any Format With HitPaw Univd (HitPaw Video Converter)
If you're looking to convert WAV files between a wide range of formats without compromising on quality, HitPaw Univd is the tool for you. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, it supports converting WAV without losing quality.
Main Featuers of HitPaw Univd
- Convert audio and video files of any format
- Convert WAV to MP3, FLAC, M4A and more without losing quality
- Convert other formats to WAV easily, such as M4A to WAV, MOV to WAV, MKV to WAV
- Download music from Spotify/Deezer/Tidal/Apple Music/Amazon Music to WAV directly
- Compress WAV files without compromising quality
- Batch convert WAV files at 120 faster speed
How to Convert WAV With HitPaw Univd
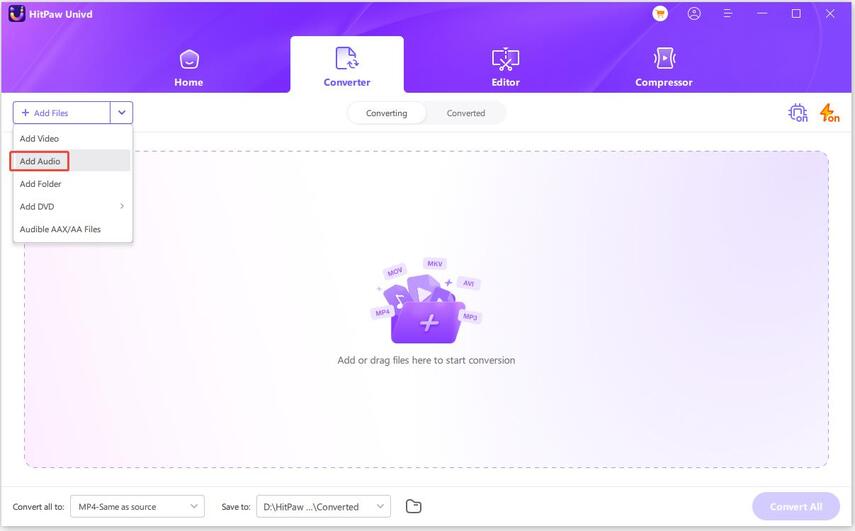
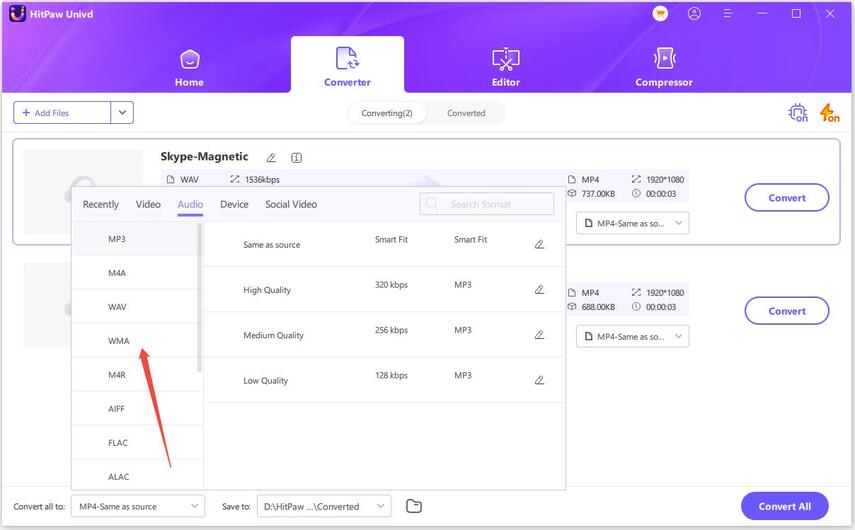
Step 1:Free install HitPaw Univd on your computer. Once the program is open, select the "Add Audio" option to import your files.

Step 2:Next, choose the output format for your WAV files. You can choose a unified output format for all imported files by clicking on "Convert all to" in the lower left corner. HitPaw Univd supports over 1000 formats and devices, so you can easily find the one that suits your needs.

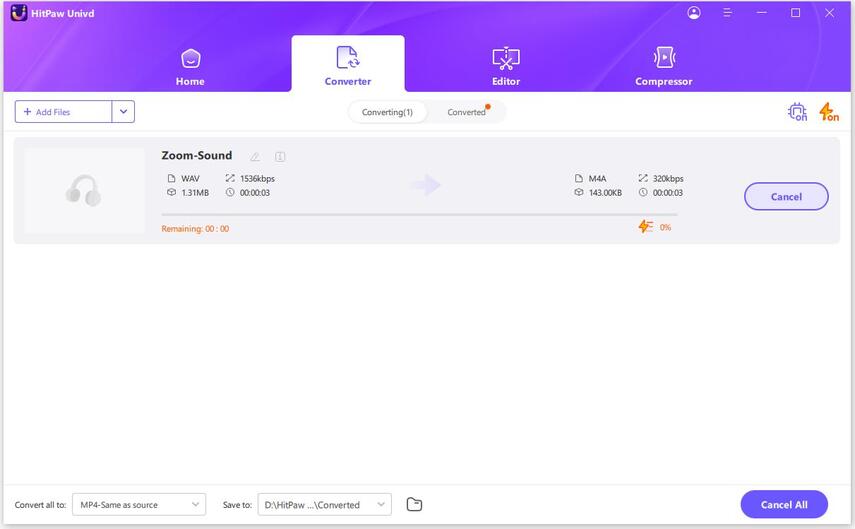
Step 3:Now, click the Convert All button to start converting WAV without losing quality.

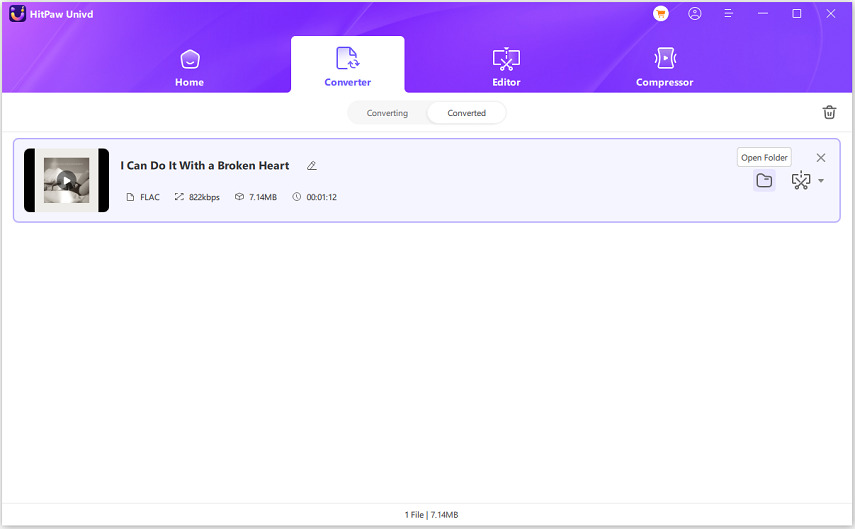
Step 4:Once the conversion is complete, navigate to the "Converted" tab at the top of the interface. Here, you will find all the converted files listed. You can click on "Open Folder" to access the converted files directly, or click on "Add" to add them to the editing list if further modifications are required.

The Bottom Line
WAV files remain a cornerstone of digital audio, valued for their uncompressed fidelity and versatility. Whether used for archival purposes, editing, or professional recording, WAV files continue to play a vital role in the world of audio engineering and content creation. You can convert any video file into WAV using HitPaw.
With HitPaw Univd, converting WAV files between various formats is a breeze. Whether you're a Windows user or a Mac enthusiast, HitPaw Univd offers a seamless experience with its intuitive interface and robust features. Say goodbye to compatibility issues and quality loss - convert WAV files effortlessly with HitPaw Univd.






 HitPaw Edimakor
HitPaw Edimakor HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Joshua Hill
Editor-in-Chief
I have been working as a freelancer for more than five years. It always impresses me when I find new things and the latest knowledge. I think life is boundless but I know no bounds.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles