The Ultimate Guide of DSD VS FLAC
Choosing the right audio format is crucial for audiophiles and casual listeners alike. In this ultimate guide, we'll delve into the differences between DSD (Direct Stream Digital) and FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec). We'll explore their unique characteristics, advantages, and potential drawbacks. Whether you're aiming for the best sound quality or optimal storage efficiency, our expert tips and tricks will help you make an informed decision in the DSD vs FLAC debate.
Part 1. DSD vs FLAC: Understanding the Basics
DSD (Direct Stream Digital)
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) is a high-resolution audio format developed by Sony and Philips for Super Audio CDs (SACDs). It uses a one-bit signal to represent audio, sampled at a very high rate. DSD 64 has a sample rate of 2.8224 MHz, while DSD 128 doubles this to 5.6448 MHz. These high sample rates aim to capture audio with greater fidelity, producing a more nuanced sound.
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC on the other hand, is a lossless compression format. It maintains the original quality of the audio while reducing file size, making it a popular choice for digital music libraries. FLAC files can be created from various sample rates, often seen as 16-bit/44.1 kHz (CD quality) and higher, such as 24-bit/96 kHz or 24-bit/192 kHz.
When comparing DSD 128 vs FLAC and DSD 64 vs FLAC, it is important to note that while DSD's higher sample rates offer theoretical advantages in capturing audio details, FLAC's flexibility in sample rates and bit depths provides a broad range of quality options, often limited by the source recording quality and playback equipment capabilities.
Comparison of DSD vs FLAC 24/192 for Audio Quality
When evaluating FLAC vs DSD quality, several key factors come into play that influence the listening experience. Both formats are designed to deliver high-fidelity audio, but they achieve this through different technologies and approaches.
Sampling Rate and Bit Depth:
- DSD: 1-bit signal, very high sampling rates (DSD 64 at 2.8224 MHz, DSD 128 at 5.6448 MHz).
- FLAC 24/192: 24-bit depth, 192 kHz sampling rate.
Sound Characteristics:
- DSD: Analog-like, warmer, smoother sound.
- FLAC 24/192: Highly accurate, detailed reproduction.
File Size and Storage:
- DSD: Larger file sizes.
- FLAC 24/192: Smaller file sizes due to compression.
In the debate of DSD vs FLAC 24/192, each format has its distinct advantages, catering to different preferences and practical needs.
Differences in File Size and Compression Between DSD and FLAC
File Size:
- DSD: Significantly larger file sizes.
- FLAC: Smaller file sizes due to lossless compression.
Compression:
- DSD: No traditional compression, resulting in larger files.
- FLAC: Uses lossless compression to reduce file size without losing audio quality.
Storage Efficiency:
- DSD: Less efficient, requires more storage space.
- FLAC: More efficient, easier to manage large music libraries.
Bandwidth:
- DSD: Higher bandwidth needed for streaming and transferring.
- FLAC: Lower bandwidth requirements, more practical for online use.
Part 2. Is DSD Better Than FLAC?
Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages of DSD over FLAC
Advantages of DSD:
- Superior Sound Quality: Many listeners find DSD to have an analog-like, warmer sound quality with smoother high frequencies.
- High Sampling Rates: DSD 64 and DSD 128 offer extremely high sampling rates, potentially capturing more audio detail.
Disadvantages of DSD:
- File Size: DSD files are significantly larger, requiring more storage space.
- Limited Compatibility: Fewer devices and software support DSD playback compared to FLAC.
- Processing Power: DSD playback can demand more from hardware, requiring high-end equipment for optimal performance.
Advantages of FLAC:
- Lossless Compression: Maintains original audio quality while significantly reducing file size.
- Compatibility: Widely supported across various devices and software platforms.
- Efficient Storage: Smaller file sizes make it easier to manage large music libraries.
Disadvantages of FLAC:
- Perceived Sound Quality: Some audiophiles feel FLAC lacks the analog warmth of DSD, though this is subjective.
- Hardware Dependent: While widely compatible, the playback quality of FLAC can vary depending on the hardware used.
Comparison of Sound Quality and Compatibility of DSD and FLAC
Sound Quality:
- DSD: Often praised for its natural, analog-like warmth and smoother sound, particularly in the high frequencies. The high sampling rates of DSD 64 and DSD 128 can capture more nuanced audio details.
- FLAC: Known for its accurate, detailed reproduction of the original recording. With 24-bit/192 kHz FLAC, the dynamic range and fidelity are excellent, though some listeners perceive it as more clinical compared to DSD.
Compatibility:
- DSD: Limited support across playback devices and software. High-end audio equipment is often necessary to fully appreciate the benefits of DSD.
- FLAC: Broadly supported by most modern audio players, software, and devices. FLAC’s versatility makes it a practical choice for a wide range of listening environments.
Explanation of Why Some Audiophiles Prefer DSD While Others Prefer FLAC
Preference for DSD:
- Sound Quality: DSD is favored for its warmer, analog-like sound, with high sampling rates providing depth and smoothness for a natural audio experience.
- High-End Equipment: Audiophiles with high-end setups may notice and prefer DSD's superior sound quality.
Preference for FLAC:
- Practicality: FLAC’s smaller file sizes and broad compatibility make it a more practical choice for everyday use.
- Accuracy: Audiophiles who value precise, detailed sound reproduction may prefer FLAC, especially at higher bit depths and sampling rates like 24-bit/192 kHz.
Part 3. FLAC vs DSD Quality: Which One Should You Choose?
Detailed Comparison of the Sound Quality of FLAC and DSD
DSD:
- Warmth and Natural Sound: Appreciated for its analog-like, warm sound by many audiophiles.
- High Sampling Rates: DSD 64 (2.8224 MHz) and DSD 128 (5.6448 MHz) capture intricate audio details, potentially providing smoother high frequencies for a more immersive listening experience.
FLAC:
- Accuracy and Detail: Known for its precise, detailed reproduction of the original recording, especially evident at higher bit depths and sampling rates like 24-bit/192 kHz.
- Lossless Compression: Maintains audio quality while reducing file size, offering high fidelity without the storage drawbacks associated with DSD.
Factors to Consider:
File Size and Storage:
- DSD: Requires significantly more storage space due to larger file sizes.
- FLAC: More storage-efficient, making it easier to manage large music libraries.
Compatibility:
- DSD: Limited support across devices and software; best appreciated on high-end audio equipment.
- FLAC: Widely supported by various devices and software, offering greater versatility.
Personal Preference:
- DSD: Preferred by those who favor a warmer, more analog-like sound.
- FLAC: Favored by listeners who prioritize detailed, accurate sound reproduction.
Recommendation of the Best Audio Converter: HitPaw Univd (HitPaw Video Converter)
HitPaw Univd is a highly recommended tool for converting between various audio and video formats. Renowned for its user-friendly interface and powerful conversion capabilities, it is a top choice for efficiently handling your media conversion needs.
Features
- Converts photos and videos to various formats with high quality.
- Downloads videos from over 10,000 sites, including YouTube, Vimeo, and more.
- Downloads music from popular platforms, ensuring you have access to your favorite tracks.
- Offers a suite of editing tools to enhance and customize your videos.
Steps
Here is How to Convert Video to Other Formats Using HitPaw Univd:
1. Import Videos: Open HitPaw Univd and click on "Add File" to import the video you want to convert.
2. Edit Video Info (Optional): Modify the video details such as title, artist, and other metadata if desired.
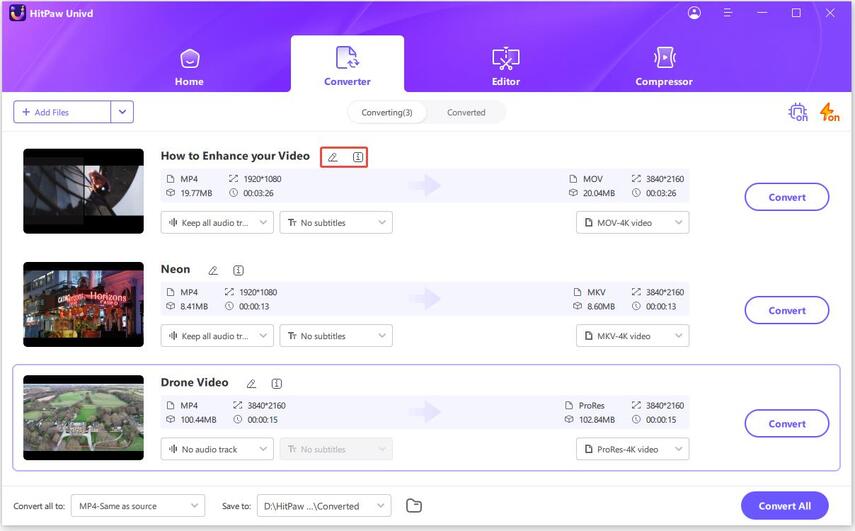
3. Add Subtitles (Optional): Insert subtitles by selecting the subtitle file to enhance your video.
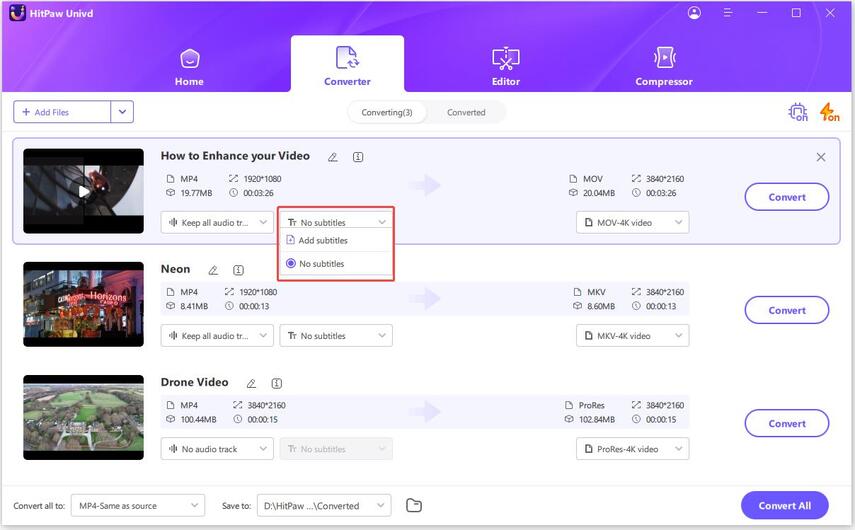
4. Select an Output Format: Select the desired output format (e.g., DSD to FLAC or vice versa) from the list of available formats.
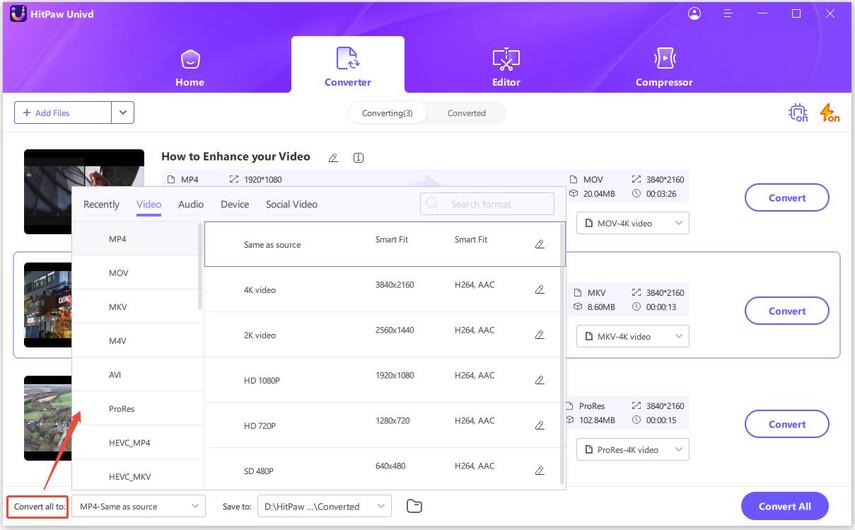
5. Convert the Video: Click the "Convert" button to start the conversion process.
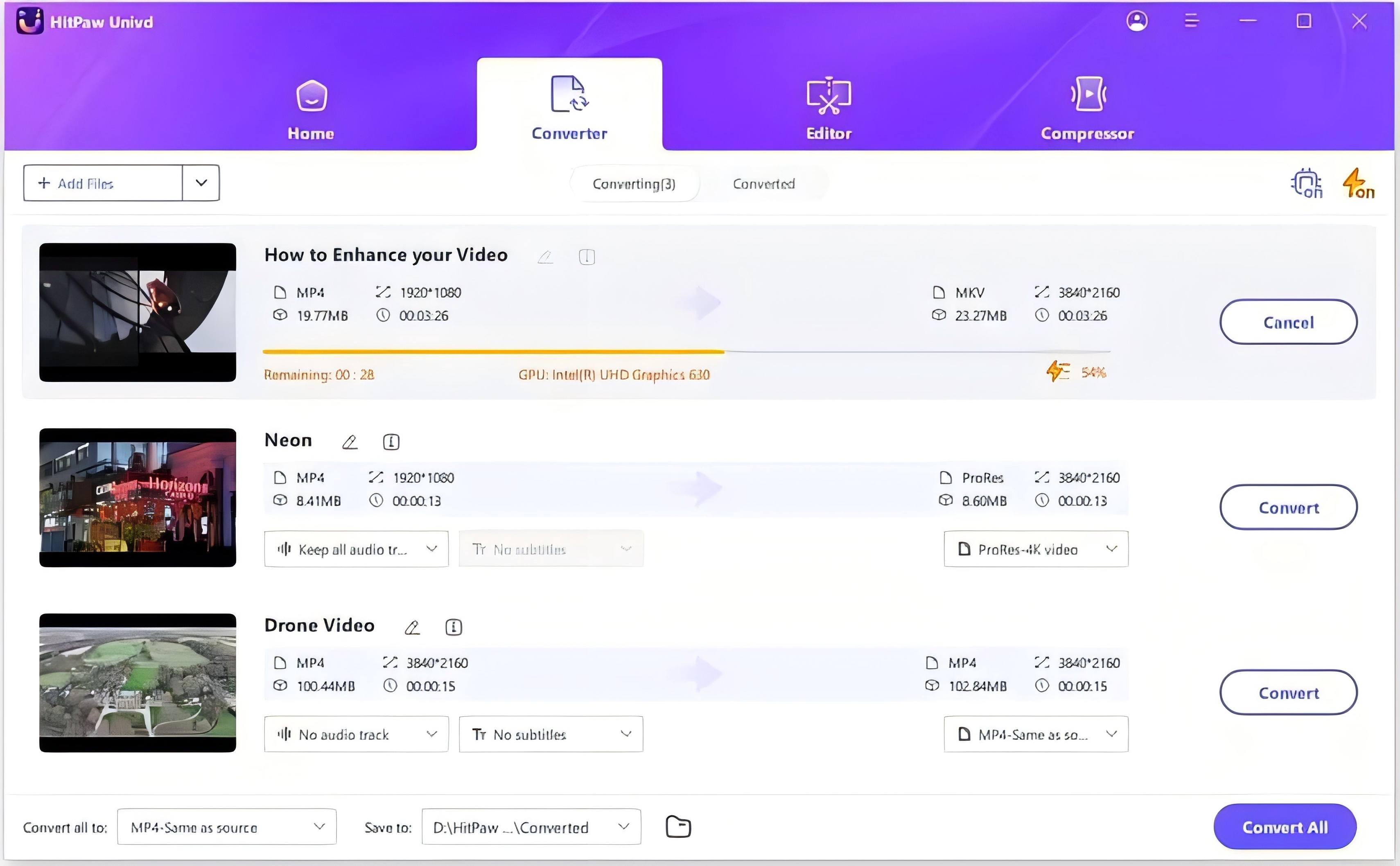
6. Access the Converted Files: Once the conversion is complete, access your converted files in the designated output folder.
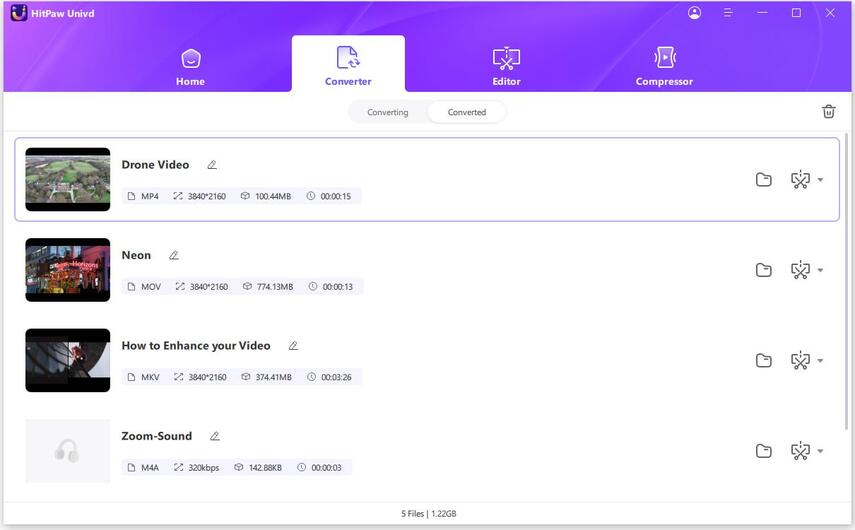
Watch the following video to learn more details:
Bottom Line
When it comes to choosing between DSD and FLAC, it ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences. DSD offers a warmer, more analog-like sound, while FLAC provides highly accurate and detailed audio with efficient storage. For those looking to convert between these formats, HitPaw Univd is a highly recommended tool, offering powerful and user-friendly conversion capabilities. Try it out to optimize your audio experience!






 HitPaw Edimakor
HitPaw Edimakor HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Joshua Hill
Editor-in-Chief
I have been working as a freelancer for more than five years. It always impresses me when I find new things and the latest knowledge. I think life is boundless but I know no bounds.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles